[2026 Full Comparison] SSD vs HDD: Which Is Better?
When choosing storage for a computer, many people compare SSD vs HDD but still feel unsure which one actually fits their needs.
Both drives store data, but they differ sharply in speed, durability, technology, and long-term reliability. With laptops, desktops, and external drives offering both options, understanding how each one works is essential for making a smart and future-proof buying decision.

What Is an SSD?
A Solid State Drive (SSD) is a storage device that uses flash memory rather than mechanical parts to store data. Instead of reading data from spinning disks, an SSD relies on integrated circuits, allowing the system to access information almost instantly. This design eliminates moving components, reduces noise, and dramatically improves speed.
How Does SSDs Work?
SSDs store data in NAND flash memory cells. When your computer requests a file, an SSD retrieves it electronically, which makes operations such as booting, launching apps, and loading games noticeably faster. The absence of physical movement also reduces latency and increases responsiveness.
- Pros of SSDs
- Cons of SSDs
-
- Extremely fast speed for booting, file transfers, and app launches.
- Silent operation because there are no spinning disks.
- Lower power consumption is great for laptops.
- Higher durability since they are resistant to drops and vibration.
-
- Higher price per GB compared to HDDs.
- Limited rewrite cycles, though modern SSDs last many years.
- Large capacities are more expensive for long-term bulk storage.
What Is an HDD?
A Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a traditional storage device that saves data on a series of spinning magnetic disks. A mechanical arm moves across the platter to read or write data.
This decades-old technology remains popular because of its cost-effectiveness and high storage capacities.
How Does HDDs Work?
Inside the drive, spinning platters rotate at high speeds (typically 5400 or 7200 RPM). The read/write head moves physically to access data locations. Because the arm must physically travel to find data, HDDs are slower and more prone to wear and tear.
- Pros of HDDs
- Cons of HDDs
-
- Much cheaper per GB, ideal for storing large amounts of data.
- High capacities, often 2TB–10TB or more.
- Great for long-term archives when extreme speed is not required.
-
- Slower performance due to mechanical movement.
- Louder operation, vibrations, and heat output.
- More fragile, easily damaged by drops.
- Higher power consumption, especially for external drives.
SSD vs HDD: Full Comparison
Choosing between HDD vs SSD depends on your priorities. The following comparison breaks down the major differences in speed, durability, gaming, and long-term usage, so you can see exactly which one fits your workflow.
Speed & Performance
SSDs deliver significantly faster speed and smoother performance than HDDs because they use flash memory rather than spinning disks. Modern SATA SSDs can reach 500–550 MB/s, while NVMe SSDs can go beyond 3,000 MB/s.
In contrast, HDDs typically transfer data at only 80–160 MB/s, as their speed is limited by the mechanical rotation of the platters. This mechanical limitation makes HDDs much slower in real-world tasks like booting Windows, opening apps, or copying large files.
Gaming Performance
When it comes to SSD vs HDD for gaming, SSDs greatly reduce loading times in games and help textures load more smoothly, especially in open-world titles. Since there are no moving parts, data loads instantly from the memory chips.
HDDs can still store and run games, but loading screens are longer, and texture pop-in may occur in modern games due to slower read speeds. HDDs struggle more as game sizes increase more than SSDs.
Long-Term Storage Capacity
HDDs typically offer much larger capacities at lower prices, making them ideal for long-term storage of photos, videos, backups, and archives. It’s common to find HDDs ranging from 1TB to 20TB.
SSDs have improved significantly in capacity, but high-capacity SSDs are still much more expensive. Most consumer SSDs range between 500GB and 4TB, making them less cost-effective for bulk storage.
Lifespan
SSDs have a limited number of write cycles, but modern models include wear-leveling and error-correction technologies that extend their usable life. Many SSDs can easily last 5–10 years under normal use.
HDDs can theoretically last as long as well, but their mechanical components wear down over time. Issues like motor failure, head crashes, and platter damage make HDDs more prone to aging-related failures.
Power Consumption
SSDs consume much less power because they rely on electronic circuits rather than motors and spinning disks. They are ideal for laptops and portable devices that need a longer battery life.
HDDs require more energy to spin platters and move read/write heads. This constant mechanical activity increases heat output and drains a laptop battery faster.
Reliability
SSDs are generally more reliable because they have no moving parts, making them resistant to drops, shocks, vibration, and general wear. They offer consistent performance even after heavy use.
HDDs are more vulnerable to physical damage and mechanical failure. Even a small accidental drop can cause platter scratches or head misalignment, leading to permanent data loss. So, HDDs lose in the SSD vs HDD reliability comparison.
Pricing
HDDs remain the most affordable option for large storage volumes, with extremely low cost per gigabyte. This makes them popular for backups, media libraries, and long-term data archives.
SSDs are more expensive, especially at higher capacities. However, prices have dropped significantly in recent years, making SSDs an accessible upgrade for users who want fast performance without overspending.
When to Use SSD or HDD?
Not everyone needs an SSD, and not everyone benefits from a large HDD. Choosing between them depends on what you prioritize in your daily computer usage.
Use an SSD if you want:
- Fast boot times and quick performance
- Better gaming experience
- Greater reliability and durability
- A quiet, low-power drive
Use an HDD if you want:
- Low-cost large storage for movies, backups, or archives
- Long-term storage without needing ultra-fast speeds
- Budget-friendly external drives
For most modern users, combining both is ideal: SSD for your system/software and HDD for massive storage. Finally, the answer to SSD vs HDD, which is better, depends on your use case, but the combination gives you the best of both worlds.
How to Recover Lost Data from SSD & HDD?
Even though SSDs and HDDs differ in structure, data loss can occur in either. Files can become inaccessible or deleted due to accidental deletion, formatting, file system corruption, virus attacks, or even sudden power failures.
This is where 4DDiG Data Recovery comes in. It is designed specifically for recovering lost data across all storage types, including internal/external SSDs, HDDs, USB flash drives, SD cards and more.
Besides, the software supports a wide range of file types, including documents, photos, videos, emails.... Even if the drive is logically damaged, inaccessible, or formatted, 4DDiG can scan the disk at a deep level to locate and restore your data.
Secure Download
Secure Download
In addition, its preview function allows you to confirm which files can be restored before proceeding, which is helpful for avoiding unnecessary recovery attempts. To recover your lost/deleted data from SSD or HDD, start by downloading and installing 4DDiG to your computer first.
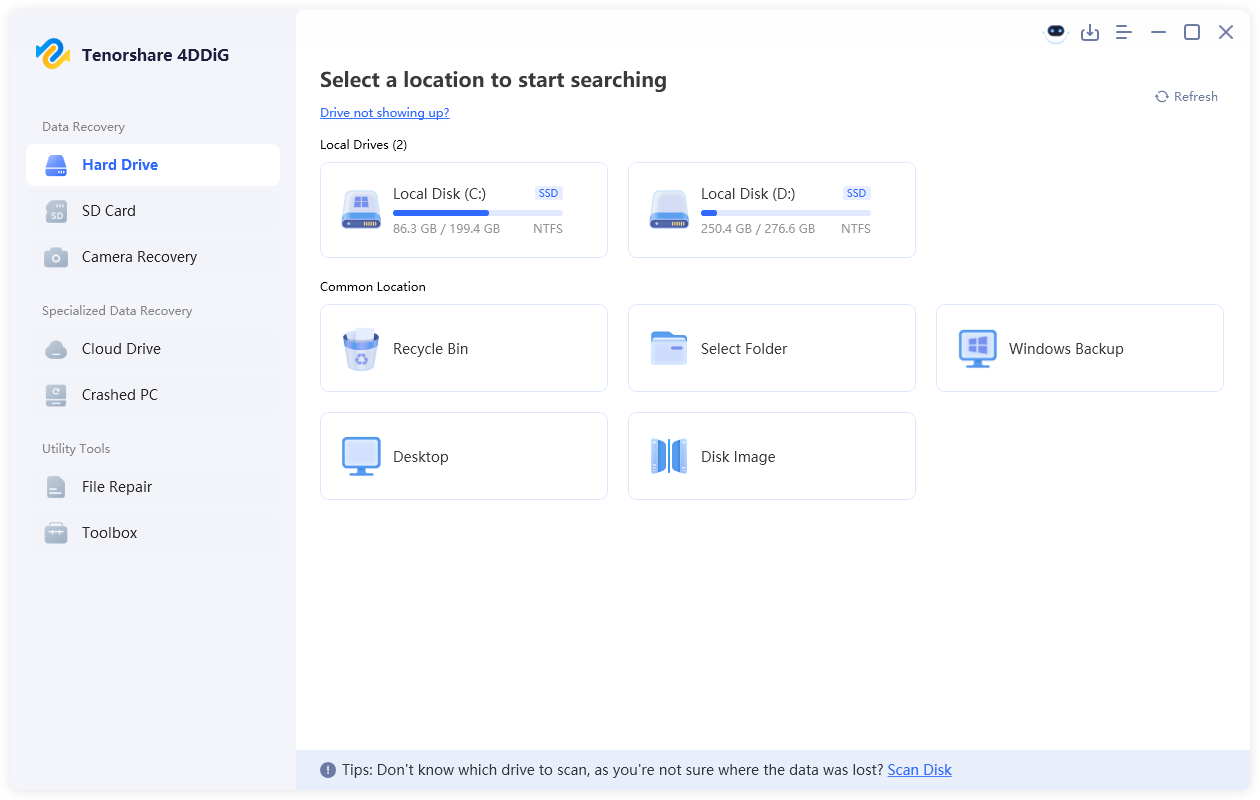
- Launch 4DDiG. Now, select "Hard Drive" from the left side and pick the drive where you lost data. For an external drive, you need to connect it to your PC. Then select the drive to begin the process.

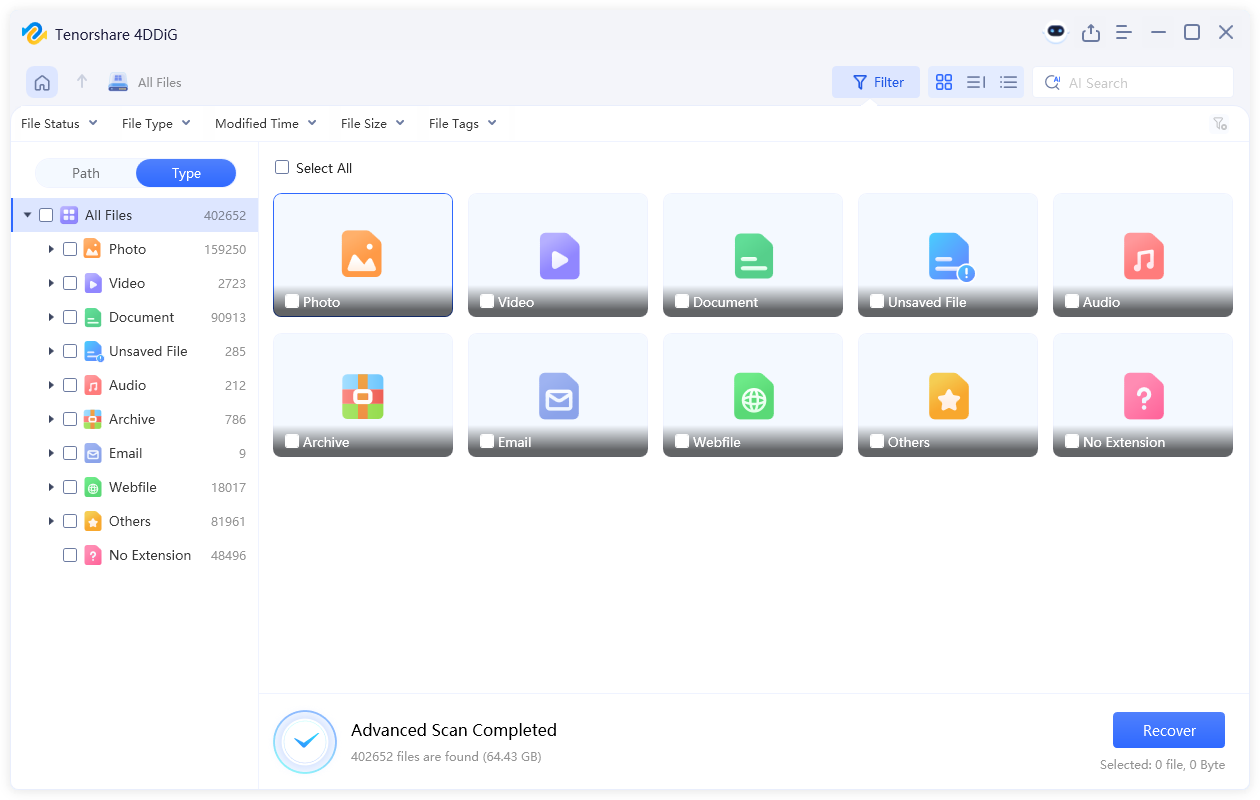
- Now, the scanning process will start, and it may take some time depending on your drive and file size. So, wait patiently, and once the scan is complete, you can use Filters or Search feature to narrow down the results.

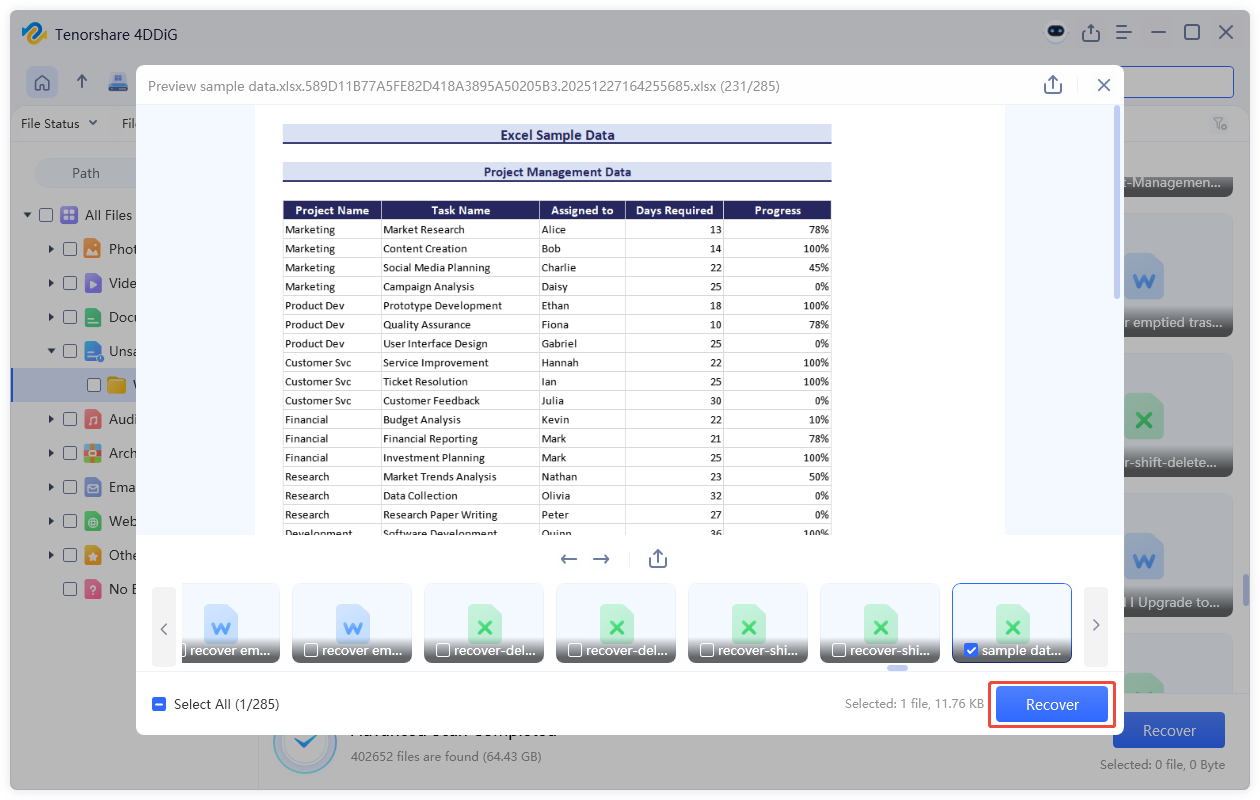
- Click on a file to have a preview. When you want to recover a file, click "Recover" to proceed.

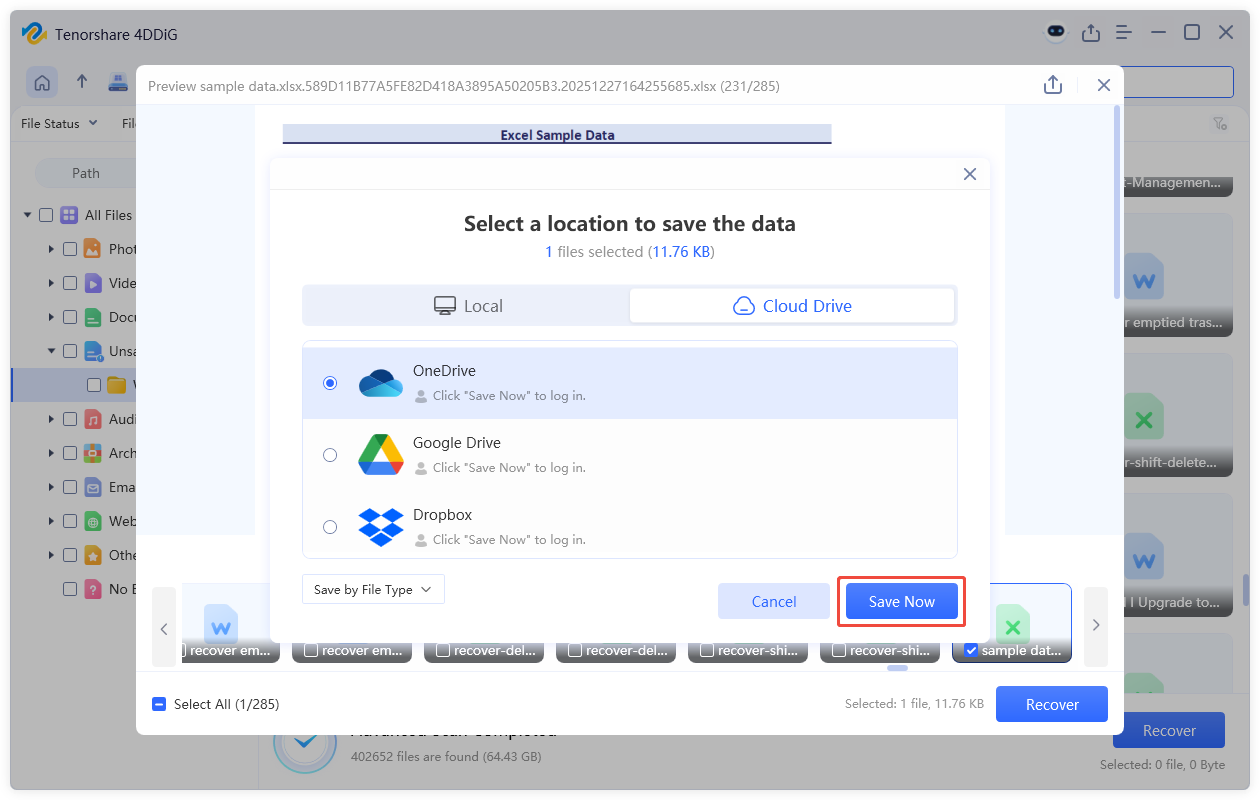
- A window will pop up asking you to choose a location to store the recoverable data. Once you've chosen a location (preferably not the original drive), click the "Save Now" to complete the process.

HDD vs SSD FAQs
Q1: What is the difference between SSD and HDD?
An SSD uses flash memory and has no moving parts, offering fast performance and high reliability. An HDD uses spinning disks and a mechanical arm to read/write data, making it slower but cheaper for large storage.
Q2: Can I use both an SSD and an HDD together?
Yes. Many users install OS and apps on an SSD for speed and use an HDD for large files, backups, or media libraries.
Q3: Can I upgrade my laptop from HDD to SSD?
Yes. It’s one of the best upgrades for speed and responsiveness. Most laptops support 2.5-inch SATA SSDs, and newer ones may support NVMe drives.
Q4: Are SSDs worth the extra cost compared to HDDs?
For the performance, yes. An SSD drastically improves speed, boot time, and overall system responsiveness. For bulk storage, HDDs still offer the best price per terabyte.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between SSD vs HDD helps you choose the right storage for your speed, capacity, and reliability needs. SSDs offer impressive performance and durability, while HDDs provide affordable bulk storage for long-term data.
If you ever lose files on either drive, tools like Tenorshare 4DDiG can help restore important documents, photos, and videos with a clear and guided recovery process. Regardless of your storage type, always keep backups and maintain your drives for the best performance.
Secure Download
Secure Download
 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok