Comment supprimer un fichier à partir de l'invite de commande Windows ?
Vous voulez savoir comment supprimer un fichier avec l'invite de commande Windows ? Suivez notre guide simple et rapide pour maîtriser cette technique !
Difficultés rencontrées lors de la suppression de fichiers ou de dossiers à l'aide de l'invite de commande sur Windows? cmd.exe, ou l’invite de commande est une commande très puissante à gérer fichiers et dossiers. Il facilite les opérations complexes telles que la suppression de fichiers via la commande del ou en supprimant des dossiers à l'aide de la commande rmdir. Mais s'il y a des erreurs commises lors de ces opérations, il y aura permanent perte de fichiers.
Dans cet article, nous allons voir comment supprimer un fichier de l’invite de commande en toute sécurité et efficacement. Nous verrons également comment récupérer les fichiers supprimés en utilisant l’outil de récupération 4DDiG pour avoir toujours un plan de secours lorsque les choses vont erreur.
- Comment récupérer des fichiers supprimés de CMD avec Tenorshare 4DDiGHOT
- Étape 1 : Localisez le dossier du fichier
- Étape 2 : Ouvrez l’invite de commande
- Étape 3 : Ouvrez l’invite de commande avec élévation de privilèges (si nécessaire)
- Étape 4 : Utilisez la commande DEL pour supprimer le fichier
- Étape 5 : Confirmez la suppression
Partie 1 : Pourquoi supprimez-vous un fichier de l’invite de commande ?
La suppression de fichiers via l’invite de commande peut sembler inutile lorsque des outils graphiques sont disponibles, mais dans certains scénarios, il devient un méthode efficace et essentielle.
Voici plusieurs raisons pour lesquelles l’utilisation de l’invite de commande peut être avantageuse :
- Supprimez rapidement plusieurs fichiers : À l’aide de caractères génériques, vous pouvez supprimer plusieurs fichiers en une seule commande, ce qui permet de gagner du temps par rapport à la suppression manuelle via l’explorateur de fichiers.
- Supprimez les fichiers tenaces ou inamovibles : Parfois, les fichiers deviennent ne répond pas ou refuse de supprimer par les méthodes conventionnelles. La commande prompt peut contourner ces erreurs pour supprimer efficacement les fichiers tenaces.
- Accéder et supprimer les fichiers cachés : Certains fichiers cachés, souvent commençant par un point (.), sont inaccessibles via l’Explorateur de fichiers. L’invite de commande vous permet de localiser et de supprimer ces fichiers cachés.
- Dépannage d’un système défectueux : Lorsque votre système tombe en panne ou l'Explorateur de fichiers devient inaccessible, l’invite de commande offre un autre méthode de gestion et de suppression de fichiers à des fins de dépannage.
- Contournez la corbeille : Les suppressions de l’invite de commande ne stockent pas de fichiers dans la corbeille, ce qui en fait une option simple pour le fichier permanent enlèvement.
La suppression de fichiers via l'invite de commande peut entraîner une perte de données. Arrêtez d'utiliser le si des erreurs se produisent et utilisez des outils tels que 4DDiG Data Recovery à restaurer les fichiers importants en toute sécurité.
Partie 2 : Comment récupérer des fichiers supprimés de CMD avec l’outil de récupération 4DDiG ?
Si vous supprimez accidentellement des fichiers importants à l’aide de commandes CMD telles que DEL, RD, ou même SHIFT + DEL et ne savez pas comment les récupérer, Tenorshare 4DDiG peut aider. Cet outil est conçu pour les situations où les méthodes manuelles de CMD provoquent perte de fichiers et rendre la récupération difficile.
Si les fichiers ont été supprimés en raison d’une erreur de commande ou d’un problème de script, 4DDiG analyse votre système pour le trouver et le restaurer. Il est particulièrement utile pour récupérer des données à partir de lecteurs ou de partitions cachés lorsque les commandes CMD ne le peuvent pas. Contrairement aux méthodes manuelles, 4DDiG protège vos fichiers écrasé et les restaure dans leur qualité d’origine.
- Analyse approfondie : 4DDiG effectue une analyse approfondie pour trouver des fichiers, même après ils ont été définitivement supprimés via les commandes CMD.
- Prévisualisation avant la récupération : Vous pouvez prévisualiser vos fichiers avant en les restaurant, en vous assurant de récupérer les bons.
- Prend en charge plusieurs types de fichiers : Il aide à récupérer un large éventail de fichiers formats, y compris les documents, les photos et les vidéos.
- Récupération en toute sécurité : 4DDiG garantit que les fichiers sont récupérés sans risque dommages supplémentaires ou écrasement.
Téléchargement Sécurisé
Téléchargement Sécurisé
Voici les étapes pour récupérer les fichiers supprimés de CMD avec 4DDiG Data Recovery:
-
Télécharger et installer
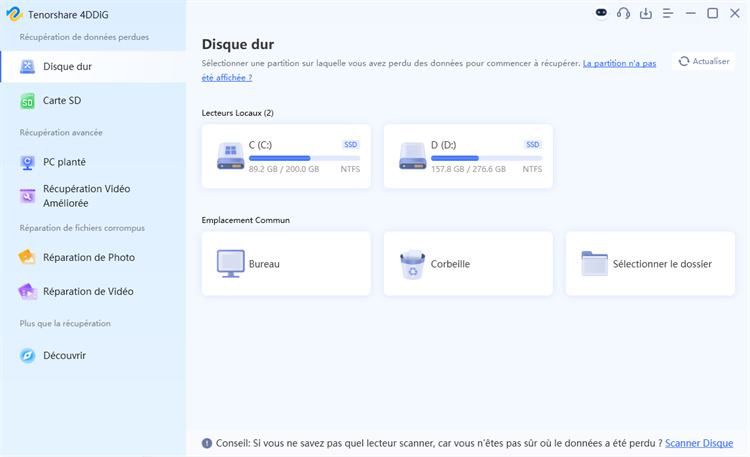
Tout d'abord, téléchargez et installez l’outil de récupération 4DDiG sur votre PC. Lancer le logiciel et sélectionnez le lecteur sur lequel les fichiers ont été supprimés de CMD. Cliquez sur le bouton « Commencer » pour commencer la numérisation.
-
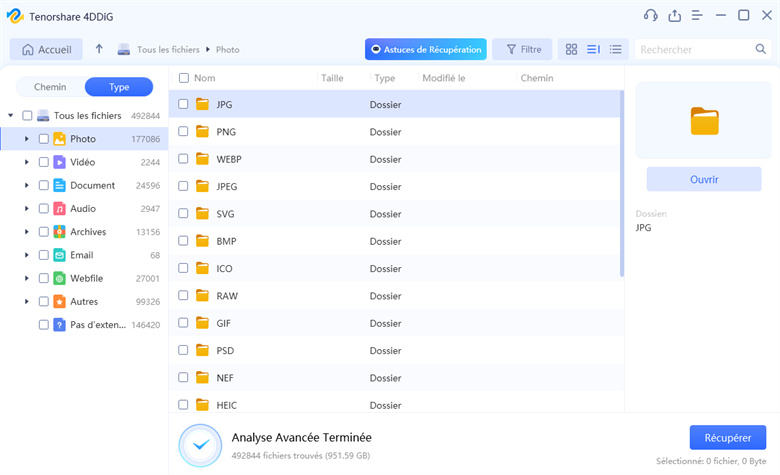
Rechercher les fichiers supprimés
4DDiG effectuera une analyse approfondie du disque sélectionné. Il recherchera pour les fichiers supprimés, y compris ceux supprimés via CMD. Attendez que l’icône processus de numérisation pour terminer.
-
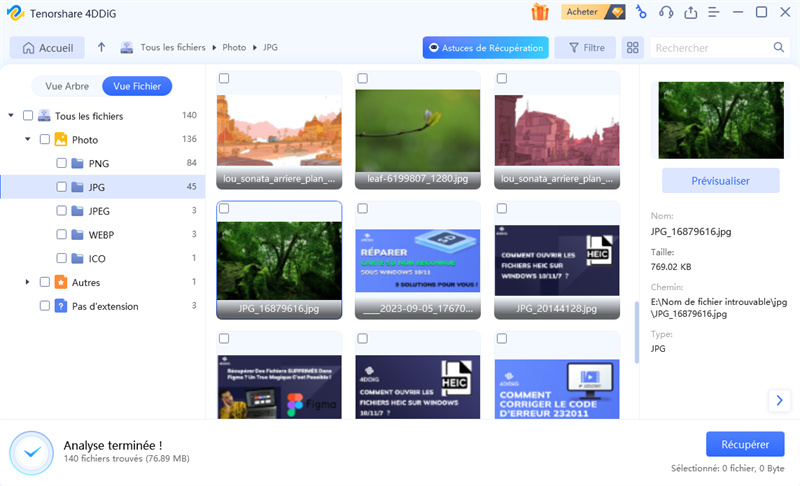
Prévisualiser et récupérer des fichiers
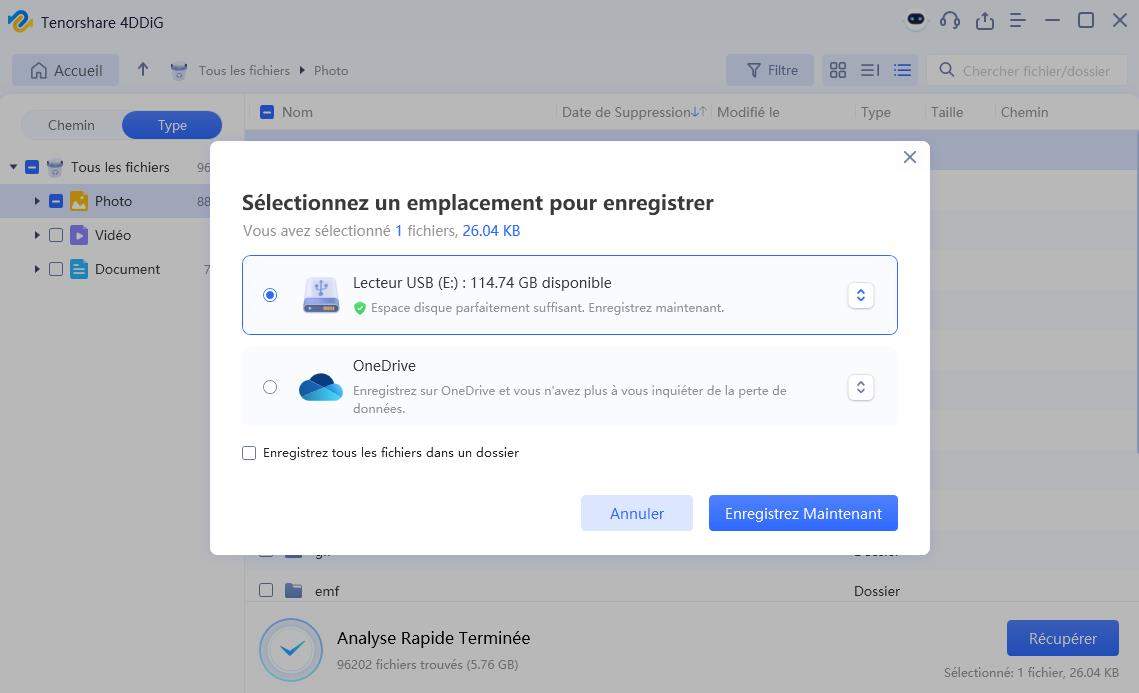
Une fois l'analyse terminée, parcourez la liste des fichiers récupérables. Prévisualisez les fichiers pour vous assurer qu’ils sont ceux dont vous avez besoin. Enfin, cliquez sur « Récupérer » pour restaurer les fichiers sélectionnés sur votre ordinateur.

Partie 3 : Comment supprimer un fichier de l’invite de commande Windows
Pour supprimer un fichier actuellement utilisé par un processus, vous devez ouvrir Invite de commande sur votre ordinateur Windows. Si le fichier est utilisé par un processus local, l’ouverture de l’invite de commande en tant qu’utilisateur standard devrait suffire.
Cependant, si le fichier est utilisé par un processus système, vous devrez ouvrir un Invite de commande élevée avec droits d’administrateur. Cela garantit que vous disposer des autorisations appropriées pour supprimer le fichier.
Étape 1 : Localisez le dossier du fichier
Commencez par localiser le dossier où se trouve le fichier. Vous n’avez pas besoin d'ouvrir le dossier, identifiez simplement son chemin. Une fois que vous avez localisé le dossier, vous pouvez passer à l’étape suivante. Cela vous permet de connaître l'exact l'emplacement du fichier, ce qui facilite sa suppression.
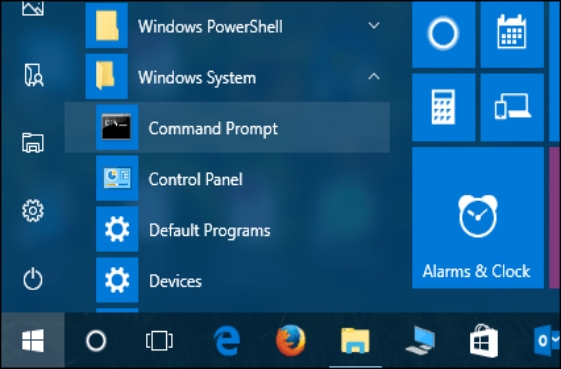
Étape 2 : Ouvrez l’invite de commande
Pour ouvrir l’invite de commande, appuyez sur Maj et cliquez avec le bouton droit de la souris sur le dossier contient le fichier que vous souhaitez supprimer. Dans le menu qui s’affiche, sélectionnez l’icône Ouvrez la fenêtre de commande ici.
Cela lancera l’invite de commande dans le dossier avec lequel vous travaillez. Toutefois, si le fichier est utilisé par un processus système, vous devrez ouvrir une invite de commande avec élévation de privilèges pour un accès de niveau supérieur.
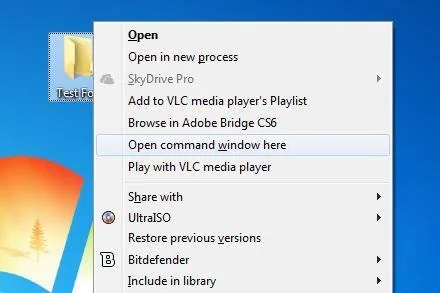
Étape 3 : Ouvrez l’invite de commande avec élévation de privilèges (si nécessaire)
Pour les fichiers utilisés par les processus système, vous aurez besoin d’une commande élevée prompt. Pour ce faire, cliquez sur le bouton Démarrer et tapez « CMD » dans le zone de recherche. Cliquez avec le bouton droit de la souris sur CMD dans les résultats et sélectionnez Exécuter en tant que administrateur.
Lorsque le contrôle de compte d'utilisateur vous y invite, confirmez votre sélection en cliquant sur Oui. Cela vous accordera les autorisations nécessaires pour supprimer les fichiers protégés fichiers.
Étape 4 : Utilisez la commande DEL pour supprimer le fichier
Une fois l’invite de commande ouverte, utilisez le DEL pour supprimer le fichier. Par exemple, tapez DEL /F nom_fichier.ext et appuyez sur Entrée. Assurez-vous de remplacer « nom_fichier.ext » avec le nom réel et l’extension du fichier que vous souhaitez supprimer.
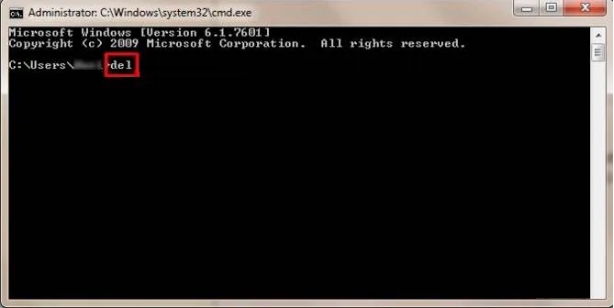
Le « /F » force la suppression du fichier, même s’il est utilisé par un processus. Attention, car la commande DEL supprime définitivement le fichier sans le déplacer dans la corbeille.
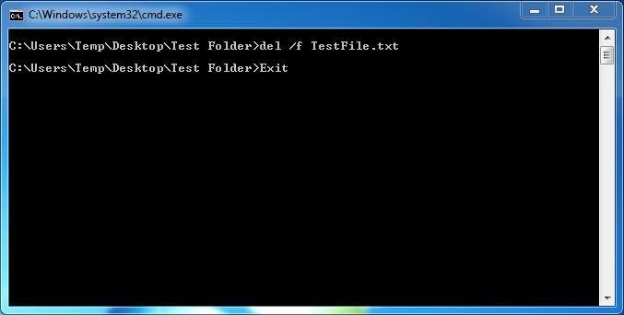
Étape 5 : Confirmez la suppression
Après avoir exécuté la commande DEL, le fichier doit être supprimé immédiatement. Vous pouvez le confirmer en vérifiant le dossier pour voir si le fichier est toujours là. S'il n'est plus visible, le fichier a été supprimé avec succès.
Une fois que vous avez terminé le processus de suppression, vous pouvez fermer la commande en toute sécurité Fenêtre d'invite. Si vous avez utilisé une invite de commande avec élévation de privilèges, il vous suffit de taper SORTIE le fermera. Si vous avez utilisé l'invite de commande standard, il vous suffit de cliquer sur le bouton Fermer.
Vérifiez toujours que vous avez sélectionné le bon fichier avant de l’utiliser cette commande. C’est une bonne idée de sauvegarder les fichiers importants avant effectuer des suppressions, juste au cas où.
Partie 4 : Conseils pour supprimer un fichier de l’invite de commande
La suppression de fichiers de l’invite de commande peut être un moyen puissant de gérer votre système, mais il est essentiel de l’aborder avec prudence. Voici quelques conseils pour vous assurer d’effectuer la tâche de manière sûre et efficace.
- Vérifiez le chemin d’accès au fichier : Avant d’utiliser la commande DEL, vérifiez le nom et le chemin d’accès du fichier. Erreur de saisie du nom ou du chemin d’accès du fichier pourrait entraîner la suppression accidentelle du mauvais fichier. Vérifiez toujours que le fichier que vous ciblez est celui que vous avez l’intention de supprimer.
- Utilisez le commutateur /F avec précaution : Le commutateur /F force la suppression d’un fichier, même s’il est actuellement utilisé. Bien que cela soit utile, soyez prudent. Il supprimera définitivement le fichier sans le déplacer dans la corbeille, ce qui rend la récupération difficile.
- Évitez de supprimer les fichiers système : Soyez très prudent lorsque vous utilisez la commande Invite à supprimer des fichiers. Suppression de fichiers système ou de fichiers utilisés par des Les processus peuvent entraîner un dysfonctionnement de votre système. En cas de doute, évitez de supprimer fichiers à partir de répertoires système tels que C :\Windows.
- Sauvegardez les fichiers importants : Sauvegardez toujours les fichiers importants avant tenter de supprimer quoi que ce soit. À l’aide d’un outil tel que l’historique des fichiers ou un Le disque externe vous permet de ne pas perdre de données critiques.
- Redémarrez votre ordinateur : Si un fichier ne peut pas être supprimé, essayez de redémarrer votre ordinateur avant d’utiliser à nouveau la commande DEL. Cela peut aider à déverrouiller n’importe quel fichier qui est verrouillé par un processus.
Partie 5 : Foire aux questions
Q1 : Qu’est-ce que la commande del dans cmd ?
Réponse : Le del dans l’invite de commande est utilisée pour supprimer des fichiers de votre ordinateur. Il supprime le fichier spécifié sans en l'envoyant à la corbeille.
Q2 : Comment supprimer un fichier dans cmd ?
Réponse : Pour supprimer un fichier dans CMD, ouvrez l’invite de commande, tapez del suivi du nom du fichier, puis appuyez sur Entrée. Assurez-vous de spécifier le chemin d’accès correct au fichier.
Q3 : Y a-t-il une commande claire dans CMD ?
Réponse : Oui, vous pouvez utiliser le cls commande dans CMD pour effacer la commande écran de la fenêtre de commande. Cette commande ne supprime pas les fichiers, elle efface simplement le l’histoire visible.
Conclusion
Dans cet article, nous avons exploré les méthodes de suppression de fichiers via Command Prompt. Bien que ces méthodes puissent être efficaces, les fichiers peuvent parfois l’être supprimé définitivement par accident. Dans ce cas, nous vous suggérons d’utiliser 4DDiG Data Recovery pour récupérer facilement les fichiers supprimés et les données perdues. Si vous avez besoin de récupérer un fichier, cet outil est facile et sûr à utiliser, et permet Bien sûr, vos fichiers importants ne disparaissent jamais vraiment.
Articles Liés
- Accueil >>
- Réparation Windows >>
- Comment supprimer un fichier à partir de l'invite de commande Windows ?