Dual Boot Windows 11 and Linux in 2026 [Complete Guide]
Dual boot Windows 11 and Linux can feel confusing when you’re not sure where to begin, especially if you’re worried about losing data or making a wrong move. Many people face the same problem, they want the power of both systems, but the setup seems too technical. If you feel stuck or nervous, don’t worry.
This guide is made for beginners and explains everything in simple, clear steps. You’ll learn how to set up both systems safely, avoid common mistakes, and feel confident using them side-by-side. Let’s get started.

Part 1: What is Dual Boot? Can You Dual Boot Windows 11 and Linux?
If you’ve ever wished you could use two operating systems on the same computer, you’re thinking about dual booting. In simple words, dual boot means installing two different systems, like Windows and Linux, on one device and choosing which one to start whenever you turn on your PC. This setup is also known as multiboot Windows and Linux, and it’s a popular choice for developers, students, and curious users who want the best of both worlds.
So, can I dual boot Windows 11 and Linux? Yes, absolutely. Windows 11 and most Linux distros can live together on the same hard drive because they use separate partitions. As long as your hardware meets basic requirements and you follow the steps carefully, both systems can run smoothly without interfering with each other.
Part 2: How to Dual Boot Linux and Windows?
Setting up a dual boot Windows and Linux system may look difficult, but the steps are easy once you understand them. The process is almost the same for Windows 10 and Windows 11, so it also helps anyone searching for dual boot Windows 10 and Linux.
Before you install anything, you must prepare your computer the right way. This makes the multiboot Windows and Linux setup smooth and helps you avoid problems like missing boot menus, storage issues, or installation errors.
Prerequisites: What You Need Before Starting
1. Supported Linux Distros
Most modern Linux distributions support UEFI systems, Secure Boot, and newer hardware, making them ideal for a multiboot Windows and Linux setup. Here are the best options:
All these distros work safely with Windows 11 and Windows 10 in a dual boot Windows and Linux setup.
2. Minimum Hardware Requirements
Although Linux runs even on old computers, dual booting both systems requires decent specs:
- 64-bit processor (Intel/AMD) with UEFI
- 4GB RAM (8GB recommended)
- 100GB free storage or more
- Separate 50GB+ space for Linux
- 8GB+ USB drive for installation
- Stable internet for updates
- Backups of important files
If your PC meets this, you’re ready to move on.
Dual Boot Linux and Windows Step-by-Step
Step 1: Back Up Your Data
Before doing anything, make sure your personal files are backed up. Dual booting is safe, but changing partitions always carries a small risk. A simple backup gives you peace of mind.
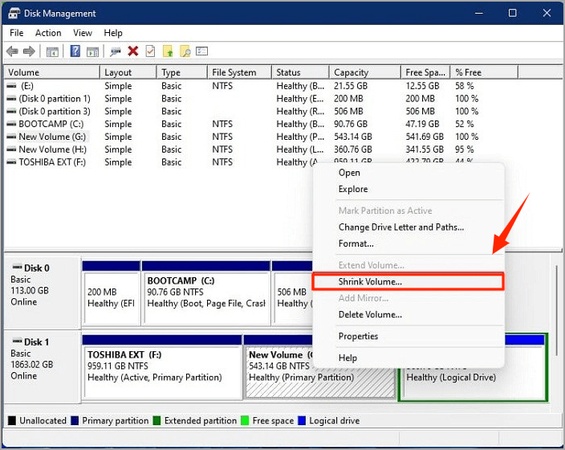
Step 2: Create Free Space for Linux
To dual boot Windows and Linux, you must first create space for Linux:
-
Press Win + X > Disk Management. Right-click your main drive (C:) and choose Shrink Volume.

-
Enter space to shrink (at least 50GB), and click Shrink. You will now see Unallocated Space, which Linux will use.
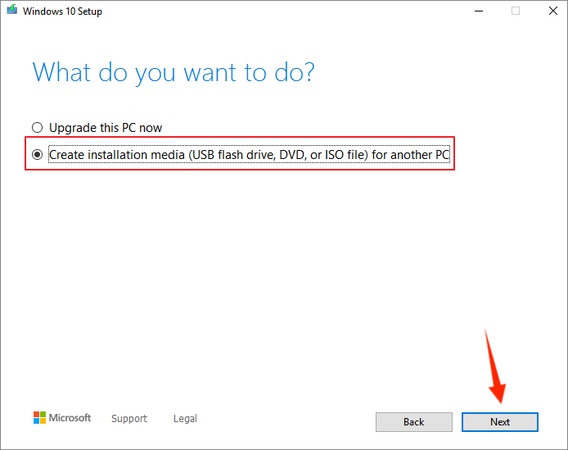
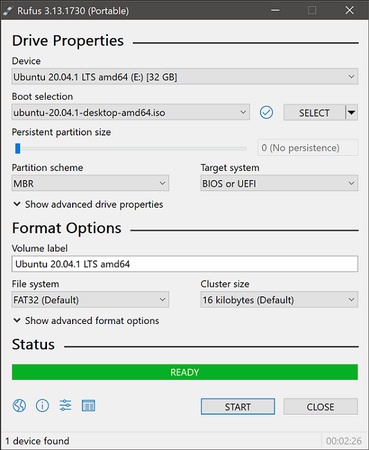
Step 3: Download and Create a Bootable Linux USB
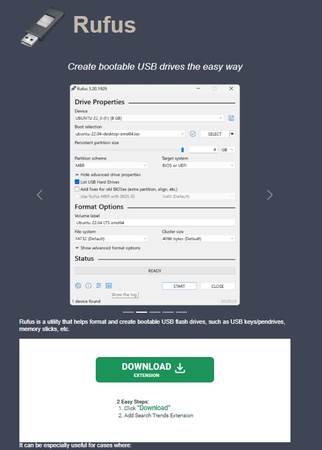
Download the Linux ISO (Ubuntu/Mint, etc.).
-
Open Rufus or balenaEtcher. Next, select your USB drive and choose the ISO file.

-
Click Start after selecting GPT + UEFI mode. After that, your Linux USB installer is now ready.
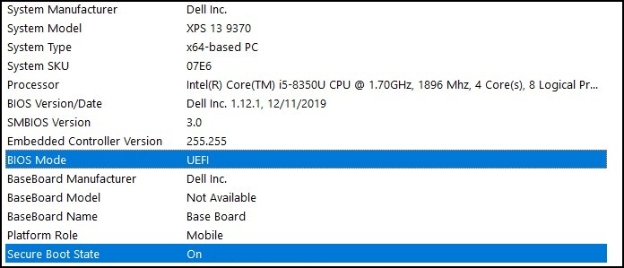
Step 4: Adjust BIOS/UEFI Settings
Restart your PC and enter BIOS/UEFI using F2, F12, Del, or Esc. You need to:
-
Enable UEFI mode (usually on by default).

-
Disable Secure Boot (recommended for compatibility)

-
Move USB Boot to the top, then save changes and exit.
Step 5: Install Linux Alongside Windows
-
Boot from your Linux USB and select Install Linux.
-
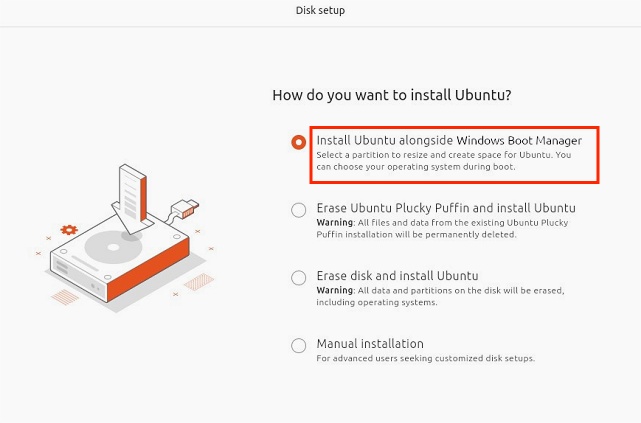
When installation type appears, choose: “Install alongside Windows Boot Manager”

-
Then, choose the partition you created earlier. Set your username, timezone, and password.
Make sure the installer installs GRUB. GRUB is the tool that manages your multiboot Windows and Linux menu.
Step 6: Restart and Choose Your OS
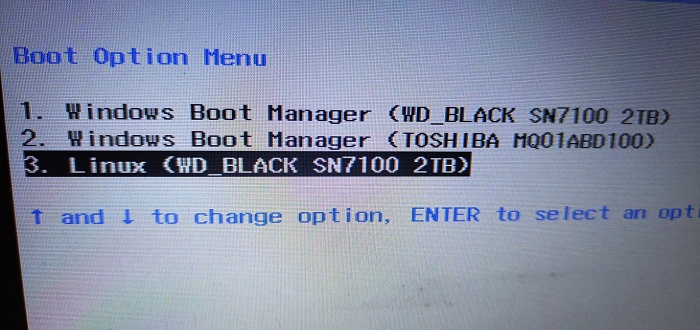
After installation, restart your system. You will now see the GRUB boot menu, where you can select:
-
Linux
-
Windows Boot Manager

This means your dual boot Windows and Linux setup is complete. If Windows doesn’t show up, boot into Linux and run: sudo update-grub. This refreshes the boot menu.
Part 3: Running Out of Space After Dual Booting? Resize Windows/Linux Partitions Safely in Minutes
Running out of space is one of the most common problems after setting up a dual boot Windows and Linux system. The easiest way to fix this is by resizing your partitions, and the safest tool for that is 4DDiG Partition Manager. It lets you extend, shrink, and move partitions without losing data, even if you’re new to managing disks.
4DDiG Partition Manager is great for beginners and people who just want a quick fix without dealing with complicated commands. For dual-boot users, it’s extremely helpful because both Linux and Windows partitions need careful handling.
Top advantages you’ll love:
- Very easy interface, perfect for beginners
- Resizes partitions without deleting data
- Fixes “not enough space” errors in minutes
- Works smoothly with Windows 10 and Windows 11
- Safe resizing even in multiboot setups
-
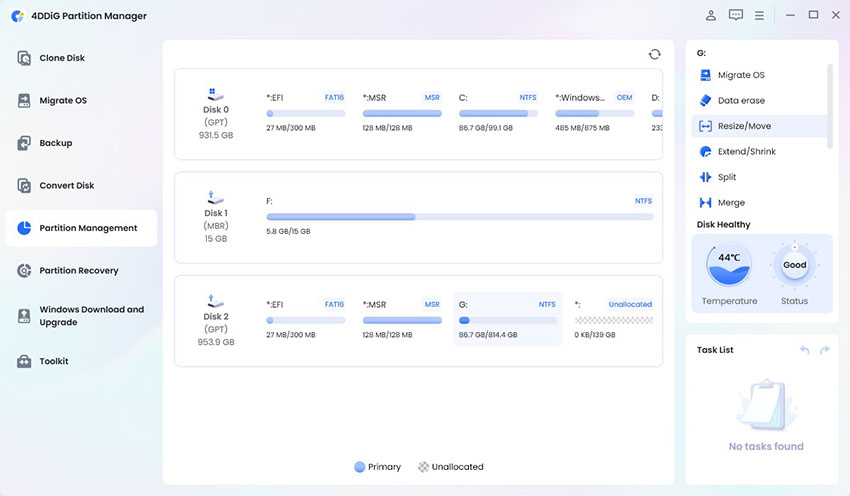
Open 4DDiG Partition Manager and click Partition Management in the left menu. Then choose the partition you want to resize or move, and click Resize/Move in the right menu.
FREE DOWNLOADSecure Download

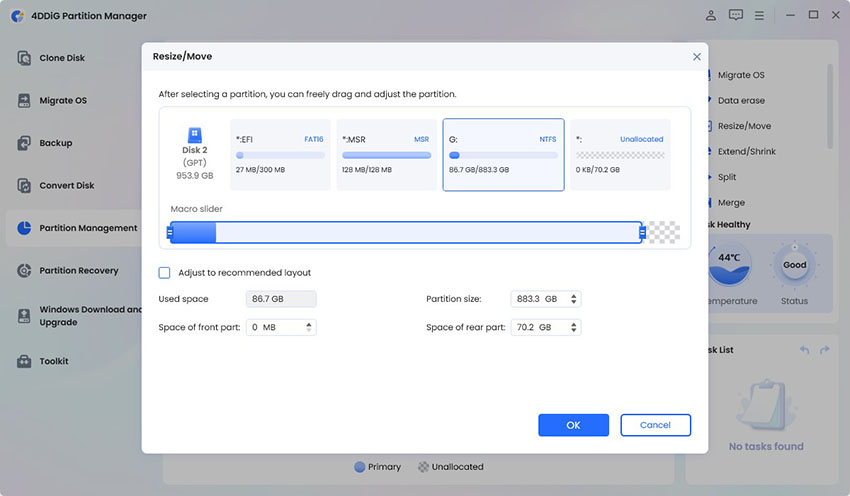
-
In the pop-up window, drag the edges of the partition to increase or decrease its size. You can also type in the exact size in GB. Preview the changes, and when satisfied, click OK to queue the operation.

-
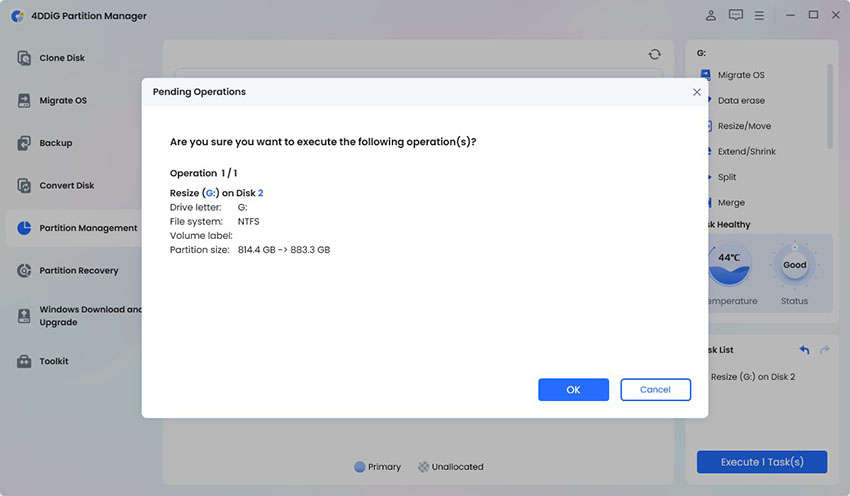
The resizing operation you queued will appear in the Task List. Click Execute 1 Task(s) and confirm by pressing OK.

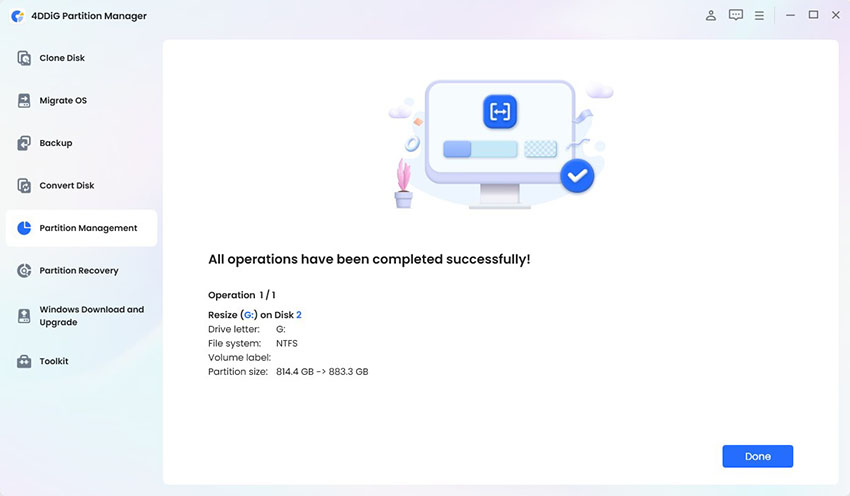
-
4DDiG will begin adjusting the partition immediately. Once the resizing is complete, click Done. Check your partitions in Windows Disk Management or Linux GParted/Storage Settings to confirm the new sizes.

More FAQs about Multiboot Windows and Linux
1. Is dual booting Linux and Windows good?
Yes, dual booting Linux and Windows is a good way to use both operating systems on the same computer. It gives you the flexibility to choose the right system for what you want to do.
2. Is it safe to have dual-boot Windows and Linux?
Yes, it is safe if you follow the correct steps. Backing up your data first is important. Installing Linux alongside Windows using the proper method and partitioning tools keeps both systems separate and secure.
3. What are the benefits of dual booting Linux and Windows?
Dual booting lets you use software that only works on Windows or Linux. It gives you better control over your computer resources, allows you to learn Linux without leaving Windows, and makes it easy to test new programs or perform tasks safely on one OS while keeping the other intact.
4. What are the disadvantages of dual booting?
The main disadvantages are that it takes up extra space on your hard drive and switching between systems requires restarting the computer. Mistakes during setup can cause boot issues, and sometimes Windows updates may affect Linux.
5. What is the best way to dual boot Windows and Linux?
The best way is to install Windows first and then Linux. During Linux installation, choose the option to install alongside Windows or use free space to create a new partition.
6. Is it possible to dual-boot Windows 11 and Linux?
Yes, it is possible. Most modern Linux versions, like Ubuntu or Linux Mint, support dual boot with Windows 11. You may need to adjust BIOS or UEFI settings, disable Secure Boot temporarily, and create space for Linux. Following a step-by-step guide ensures the process is safe and smooth.
Conclusion
Setting up a dual boot Windows 11 and Linux system is a great way to use both operating systems on one computer. With proper preparation and careful installation, you can switch between Windows and Linux safely and easily.
If you run out of space or need to change partition sizes after dual booting, 4DDiG Partition Manager is a great tool to use. It helps you resize, move, and manage partitions quickly and safely, even if you are new to it. Using this tool makes managing your dual-boot system simple and worry-free.
Secure Download


 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok