What Is Vmmemwsl? Fix High Memory Usage in Windows 11
Vmmemwsl using too much memory or CPU on your computer? Many Windows 11 users face the same issue. When vmmemwsl high memory or vmmemwsl high CPU usage happens, the system becomes slow, and it can be confusing if you don't know what is vmmemwsl.
Don't worry as this process is not harmful, and there are easy ways to fix it. In this guide, we'll explain what vmmemwsl is, why it uses so many resources, and show you simple steps to reduce the load and make your PC fast again. So, let's get started.
Part 1. What Is Vmmemwsl?
If you're wondering what is vmmemwsl, it's a system process in Windows that comes from using Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) or Docker Desktop. This process acts as a bridge between your Windows system and the virtual Linux environment. When you run Linux distributions or Docker containers, vmmemwsl is the one managing the virtual machine behind the scenes.
The vmmemwsl process shows up in Task Manager and may use a lot of memory and CPU because it's running all the Linux-based operations inside Windows. Simply put, it is not a virus or harmful software, it's an important tool for developers and advanced users.
So, what is VMMEM used for? It is mainly used to power virtual environments like Docker containers and Linux distributions on Windows. Without it, those apps wouldn't be able to run properly.
Part 2. Why Does Vmmemwsl Take High RAM & CPU Usage?
If you see vmmemwsl high memory or high CPU usage in Task Manager, it usually means the virtual environment is using more resources than expected. Let's look at the main reasons:
-
Running Docker Containers
When you use Docker Desktop, Windows launches vmmemwsl to run containers. Each container needs its own share of memory and CPU. This is why you often see Windows Docker vmmemwsl memory taking up a large portion of system resources. -
Multiple Linux Distributions in WSL
If you have more than one WSL distribution running in the background, vmmemwsl manages them all. This can lead to vmmemwsl high RAM usage, especially if you're working with heavy development tools or servers. -
Background Services & Processes
Even if you're not actively using WSL or Docker, background services may still be running. This makes you wonder, why is vmmem taking so much RAM? The answer is usually hidden processes or services running inside the Linux environment. -
Unoptimized Configuration
By default, WSL and Docker can take as much memory and CPU as they want. Without limits, the vmmemwsl process may end up using far more resources than necessary.
✅ How to Check CPU Usage on Mac [Best Mac App to Check CPU Usage]
Part 3. How to Limit Vmmemwsl Memory Usage?
Here are four effective methods to reduce the load of the vmmemwsl process, especially when you notice vmmemwsl high memory or want to release memory from vmmemwsl. Each method includes clear steps you can follow suggestions to help you.
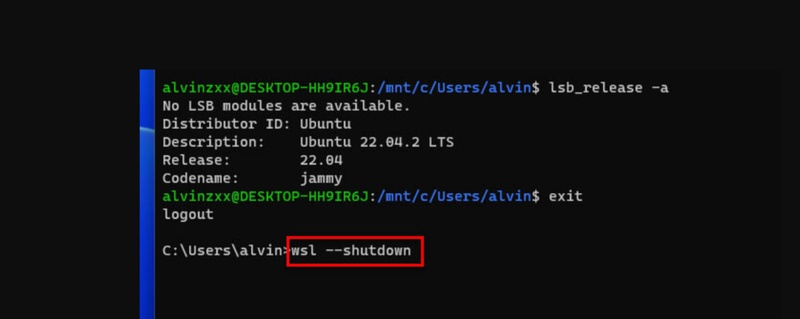
Method 1: Shut down WSL
Good first step: shutting down WSL stops all Linux distributions and frees up memory used by the vmmemwsl process.
Steps:
-
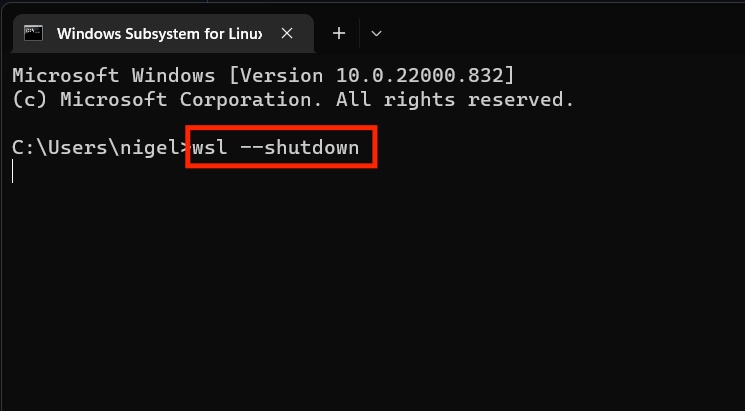
Open PowerShell or Command Prompt as Administrator.
-
Run the command: wsl --shutdown.

This will stop all WSL 2 distributions currently running.
-
Wait a moment and then open Task Manager. Look for the vmmemwsl or Vmmem process, its memory and CPU usage should drop significantly.
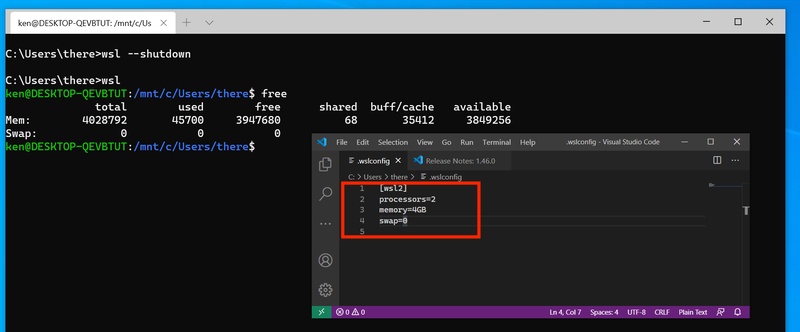
Method 2: Edit .wslconfig to limit memory/CPU
If vmmemwsl high ram usage continues, you can set resource limits via the .wslconfig file. This stops WSL from using more than your defined memory or CPU cores.
Steps:
-
Go to your Windows user profile folder: open File Explorer, type %UserProfile% in the address bar.
-
Check if a file named .wslconfig exists. If not, create one. Make sure it's not .wslconfig.txt.
-
Open .wslconfig with Notepad or another text editor. Add or edit settings under the [wsl2] section. For example:
#Limits VM memory to use no more than 4 GB, this can be set as whole numbers using GB or MB
memory=4GB
#Sets the VM to use two virtual processors
processors=4

Save the file.
-
To apply the changes, shut down WSL using wsl --shutdown, then start it again (launch any distro or Docker) so that the new limits take effect.
Method 3: Disable unnecessary containers or background services
Often Docker containers or Linux services running in the background contribute significantly to vmmemwsl high memory and high CPU usage. Turning off what you don't need helps.
Steps:
Open Docker (if using Docker) or your terminal/distribution.
-
List running containers or services:
- For Docker: use docker ps to see containers.
- For WSL: run wsl -l -v to see which distributions are running.
-
Stop containers or services you're not using:
- Docker: docker stop <container_name_or_id>
-
WSL distro: wsl --terminate
to stop a specific distribution.
-
Once you disable or terminate these, run wsl --shutdown to ensure no leftover processes are keeping vmmemwsl alive.
Method 4: Restart Docker Desktop / WSL service
If changes aren't taking effect or vmmemwsl seems stuck consuming resources, restarting the service or app often helps.
-
Close Docker Desktop entirely (not only exit, but quit) if you're using it.
-
Open PowerShell as Administrator. Run “wsl --shutdown” to stop all WSL distributions.

If needed, restart the LxssManager service in Windows Services:
Press Win + R, type services.msc, enter.
-
Find LxssManager, right-click > Restart. This service handles WSL instances.
-
Then launch Docker/Desktop or open a WSL distro to see if vmmemwsl usage remains lower.
Part 4: How to Resize and Extend Your Partition?
Running out of disk space can be frustrating, especially when it causes vmmemwsl process to use more resources than it should. If your system drive is low, WSL and Docker virtual disks (ext4.vhdx) struggle to expand, which often results in slowdowns or vmmemwsl high memory/disk usage. The easiest fix? Free up space and manage your partitions properly.
That's where 4DDiG Partition Manager comes in. Unlike the built-in Disk Management tool, 4DDiG makes resizing and extending partitions simple, safe, and beginner-friendly. Whether you want to shrink, extend, or merge partitions, you can do it with just a few clicks, no risk of losing your files.
Now let's learn how to resize and extend a partition.
Secure Download
-
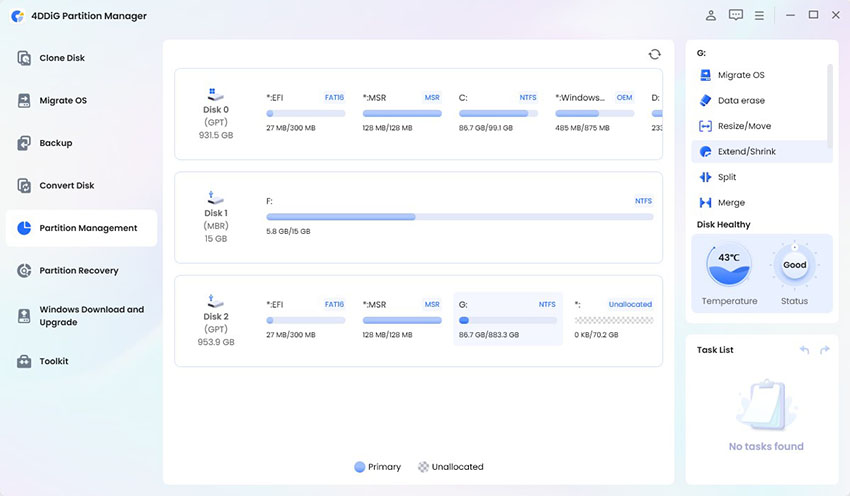
Download and launch 4DDiG Partition Manager. From the left panel, choose Partition Management. Then choose the partition you want to extend or shrink and select "Extend/Shink" from the right menu.

-
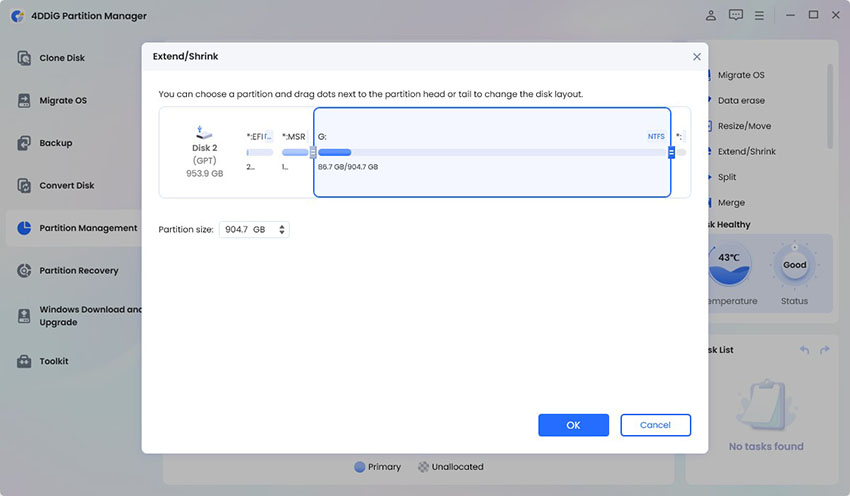
Drag the border of the partition. Move it right to add more space, move it left to make it smaller.Then click OK.

-
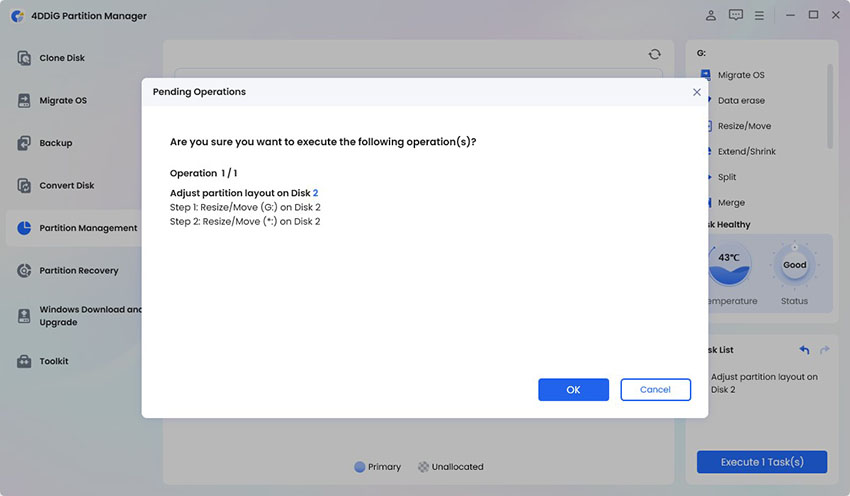
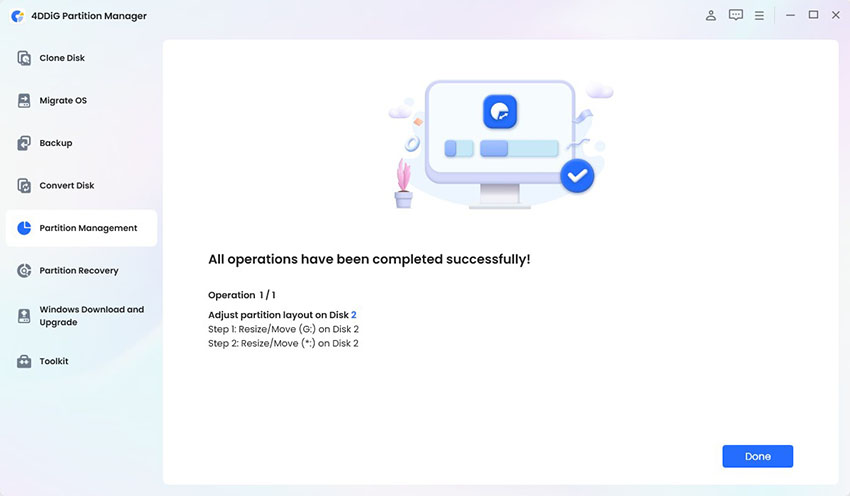
The change will appear in the task list. Click Execute 1 Task(s) and press OK to start.

-
It takes time depending on the space you add, and do not close the program while it's running.When it's done, click Done. Your partition is now successfully extended or resized.

More FAQs about Vmmemwsl
Is it safe to disable vmmemwsl?
Yes, it is safe if you are not using WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) or Docker at that time. The vmmemwsl process is needed for running Linux apps and containers. If you stop it while they are running, your apps may crash. The safe way is to run wsl --shutdown in PowerShell or close Docker Desktop first.
Why is vmmemwsl using disk so heavily?
This usually happens when WSL or Docker is doing a lot of file work, like building code, running databases, or syncing files. Sometimes, background containers also cause high disk use. To fix this, stop unused containers, restart WSL/Docker, or move heavy tasks to another drive.
Conclusion
Vmmemwsl high memory or CPU usage can slow down your PC, but now you know how to fix it. We explained what is vmmemwsl, why it uses so many resources, and how to control the vmmemwsl process with easy steps like shutting down WSL or editing settings.
For storage issues, 4DDiG Partition Manager helps you resize and extend partitions safely. It's simple, effective, and keeps your system running smoothly. Explore more 4DDiG tools to make managing your computer even easier.
Secure Download
 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok