PCIe 3.0 vs 4.0: Which is Better in 2026 (SSDs)
Are you in the market for a new SSD but feeling overwhelmed by the technical jargon surrounding PCIe versions? Don't worry; you're not alone! Choosing the right PCIe version for your SSD can be confusing, especially with the release of PCIe 4.0.
In this article, we will simplify the decision-making process by comparing PCIe 3.0 vs PCIe 4.0 and helping you determine which is better suited for your needs. Whether you're a casual user or a tech enthusiast, we've got you covered. So, let's dive in and explore the differences between these two PCIe versions to find the best fit for your SSD requirements.
So, let's get started.
Part 1: What are PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0?
Before we can get started with PCIe 3.0 vs PCIe 4.0, it's better to first understand both of them in detail, like what they are, key features, etc.
1. PCIe 3.0
PCIe 3.0 is a way for parts like graphics cards and SSDs to connect to a computer's main part, called the motherboard. It's faster than the older PCIe 2.0 and can move data more quickly. It can transfer up to 15.75 GB of data in one direction every second if it's plugged into a special slot called x16.

Some key features of PCIe 3.0 include:
- Bandwidth: PCIe 3.0 offers a per-lane data transfer rate of 15.75 Giga transfers per second (GT/s), effectively doubling the bandwidth compared to PCIe 2.0.
- Backward Compatibility: PCIe 3.0 is backward compatible with PCIe 2.0 and PCIe 1.0, allowing older devices to work with newer motherboards.
- Power Efficiency: PCIe 3.0 introduces power-saving features, including a lower standby power requirement and the ability to dynamically scale power to individual devices.
2. PCIe 4.0
PCIe 4.0 is the newest version of the PCIe connection. It's even faster than PCIe 3.0 and has more bandwidth. It can transfer up to 31.51 GB of data in one direction every second if it's plugged into a special x16 slot. This is really good for devices that need to move data really quickly, like super-fast storage drives and really fancy graphics cards.

Key features of PCIe 4.0 include:
- Increased Bandwidth: PCIe 4.0 doubles the bandwidth per lane compared to PCIe 3.0, providing a data transfer rate of 31.51 GT/s.
- Enhanced Performance: The increased bandwidth of PCIe 4.0 allows for faster communication between the motherboard and devices, resulting in improved overall system performance.
- Forward and Backward Compatibility: PCIe 4.0 is backward compatible with previous generations, meaning that PCIe 3.0 devices can be used in PCIe 4.0 slots, albeit at their maximum supported speed.
Part 2: Difference Between PCIe 3 and 4
So now you know about both PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0, it's time to discuss are differences between them.
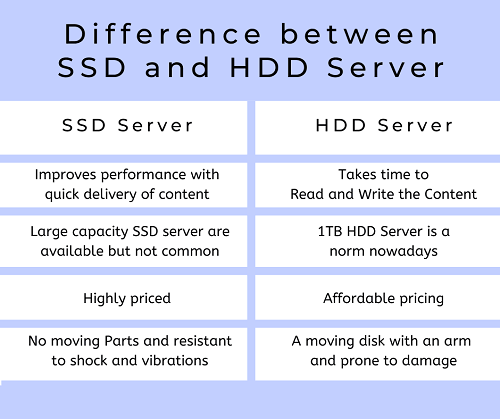
1. PCIe 3.0 vs 4.0: Architecture and Design
The first and most important difference between PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0 is their architecture and design. You can clearly see the difference in their design in the picture above.
Besides, PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0 have different architectural designs. PCIe 3.0 uses an 8b/10b encoding scheme, which means that 8 bits of data are encoded into a 10-bit symbol. This encoding scheme introduces some overhead, reducing the effective data transfer rate. On the other hand, PCIe 4.0 uses a more efficient 128b/130b encoding scheme, reducing the encoding overhead and allowing for higher data transfer rates.
2. PCIe 3.0 vs 4.0: Speed
Another major difference between PCIe 3.0 and 4.0 is the speed or bandwidth. PCIe 3.0 offers a per-lane data transfer rate of 8 GT/s, while PCIe 4.0 doubles that to 16 GT/s per lane. This doubling of bandwidth enables PCIe 4.0 to achieve higher data transfer rates, resulting in improved performance for devices connected to it.
3. PCIe 3.0 vs 4.0: Compatibility and Availability
Besides design and speed, another big difference between PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0 is their compatibility and availability. PCIe 4.0 is backward compatible with PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 2.0, meaning that PCIe 3.0 devices can be used in PCIe 4.0 slots, although they will operate at their maximum supported speed.
However, PCIe 4.0 devices require a compatible motherboard with PCIe 4.0 slots to take full advantage of the increased bandwidth. As of now, PCIe 4.0 support is more limited compared to PCIe 3.0, with fewer motherboards and devices available on the market.
So these are the major differences between both types of SSDs, but what impact do PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0 have on the performance of SSD? Which type of SSD performs better?
Let's discuss this in detail.
Part 3: What Impact Do PCIe 3.0 and 4.0 Have on the Performance of SSD?
The impact of PCIe 3.0 and 4.0 on SSD performance is significant. PCIe 4.0 offers higher bandwidth and data transfer rates compared to PCIe 3.0. This translates to faster read and write speeds for SSDs connected to a PCIe 4.0 interface. With PCIe 4.0, SSDs can deliver improved performance, reduced loading times, and enhanced overall system responsiveness.
It is particularly beneficial for high-performance SSDs like NVMe drives that can fully utilize the increased bandwidth.
However, it's important to note that both the SSD and the motherboard need to support PCIe 4.0 to achieve its maximum speed advantage. If the SSD or motherboard is limited to PCIe 3.0, the SSD will operate at the maximum speed supported by that interface.
Bonus tip: Is It Possible to Upgrade to a PCIe 4.0/3.0 SSD without Reinstalling OS?
So if you have finally decided to upgrade to a PCIe 4.0 or 3.0 but are concerned about operating system installation, we have good news for you. You can upgrade to a PCIe 3.0 or 4.0 without reinstalling the operating system with the help of the 4DDiG Partition Manager tool.
All you have to do is follow the steps given below and successfully upgrade to a PCIe 3.0 or PCIe 4.0 without reinstalling OS.
-
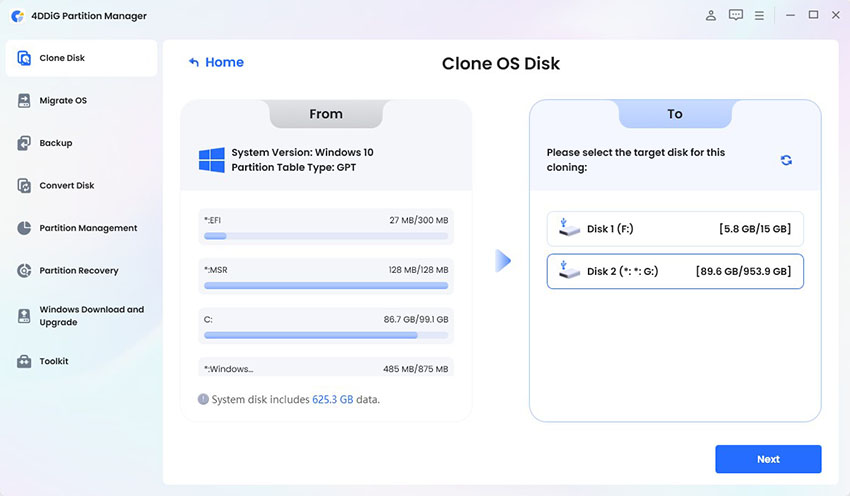
First of all, connect your new SSD, whether it is PCIe 3.0 or PCIe 4.0, to your computer and download and install the 4DDiG Partition Manager tool. After installing, launch the tool and go to Clone Disk, and select Clone OS Disk.
FREE DOWNLOADSecure Download

-
Now select the newer SSD that you have just installed and hit the Next button.

-
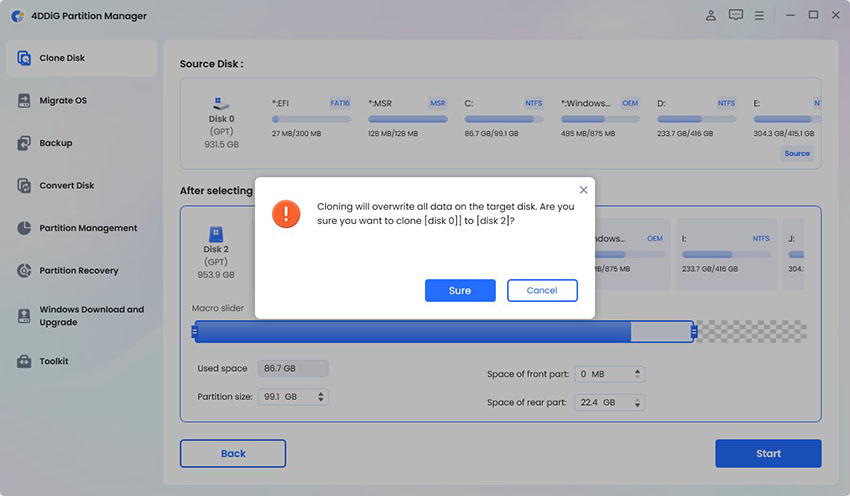
Start the migration, you will see a Pop-Up warning message, so hit the Sure button to continue.

-
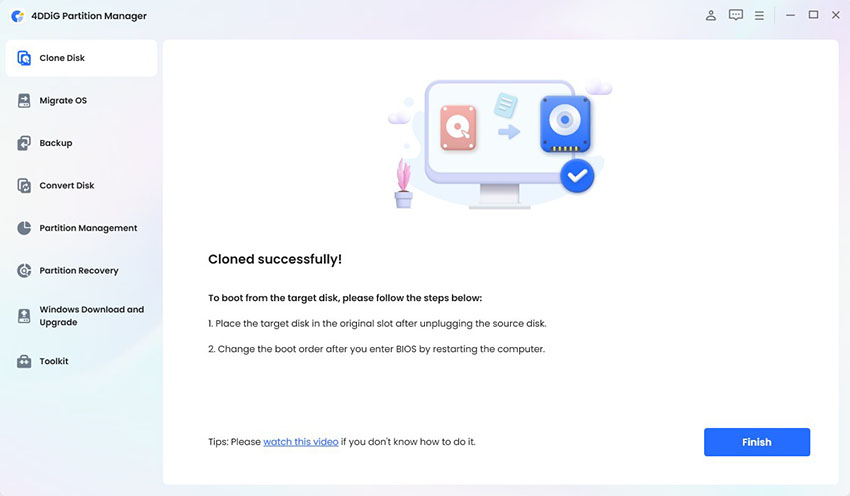
This will start the OS migration process, and you will have to wait for the process to be completed. Once the process is completed, hit the Finish button.

That's how you can successfully upgrade to PCIe 3.0 or 4.0 SSD without reinstalling the OS.
Final Thoughts
So this is all about PCIe 3.0 vs PCIe 4.0. Both are great and provide different advantages. By reading their comparison, you must be interested in upgrading your PC to PCIe 3.0 or PCIe 4.0 SSD based on your needs. Whether you upgrade your PC with PCIe 3.0 or PCIe 4.0 SSD, the 4DDiG Partition Manager tool will help you migrate your OS to the new SSD without reinstalling the OS. So, don't hesitate to try it!

 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok