You Don't Have Enough Free Space in var/cache/apt/archives/: What It Means & 3 Fixes
When managing a Linux system, especially on servers or devices with limited storage, package management can sometimes show unexpected errors. One of the most common and frustrating issues happens during updates or software installations.
You might suddenly encounter the message: "you don't have enough free space in /var/cache/apt/archives/". This error highlights a space shortage in a critical directory, and resolving it is key for proper system performance and updates. Let’s see how.
Part 1. What Does "You Don't Have Enough Free Space in var/cache/apt/archives/" Mean
The error "not enough free space in /var/cache/apt/archives" means your system's APT cache directory is full. This prevents package installations or updates until space is freed.
➡️ What Is Var Cache Apt Archive
/var/cache/apt/archives/ is a directory used by Debian-based Linux systems to store downloaded package files. These files are cached, so they don’t need re-downloading during future installations or updates. Over time, this folder can grow large and consume valuable disk space.
➡️ What Error Means & What Causes It
This error usually occurs during system updates or when installing new packages using APT on Debian-based systems. It indicates that the APT cache directory, located at /var/cache/apt/archives/, doesn’t have enough disk space to store additional package files. Since APT temporarily saves all .deb files during installations, the cache can grow over time, especially if you don’t manage it.
There are many factors that contribute to this problem. One is APT’s default policy of retaining every downloaded package file, even after installation. On systems like Ubuntu, Kali, or Raspberry Pi, outdated or unused packages may accumulate quickly. Additionally, if the /var/cache/apt/archives/partial directory is missing, it can disrupt APT’s operations.
Part 2. Best Way to Delete Duplicate Files to Free Up Space for var/cache/apt/archives/
If you're constantly running into storage issues like APT-related errors on Linux, it’s time to look beyond just clearing cache folders. One overlooked cause of low disk space is duplicate files, especially large, unnecessary copies in directories like EpicGamesLauncher and other user folders.
That’s where 4DDiG Duplicate File Deleter comes in. It uses AI and quickly scans and removes duplicate files from internal drives, external storage, SD cards, and even cloud drives on both Windows and Mac systems. With smart algorithms, customizable search settings, and real-time duplicate reminders, 4DDiG provides an easy way to reclaim disk space if you are facing the issue of not enough free space in /var/cache/apt/archives.
How to Use 4DDiG Duplicate File Deleter to Free Up Space
Here's how to use it to delete duplicate files and optimize your storage:
Secure Download
Secure Download
-
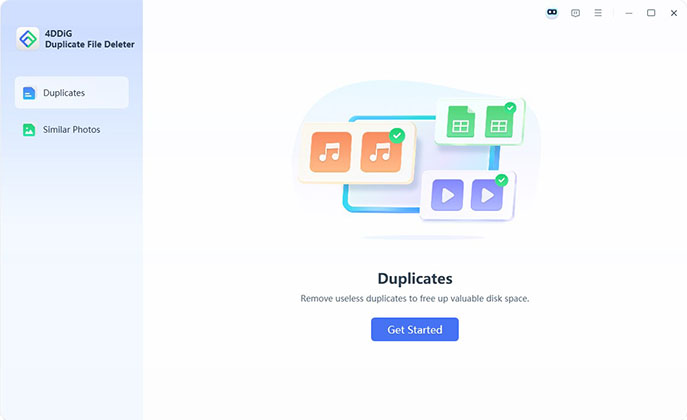
Launch 4DDiG and Start Duplicate Scan
Open the installed 4DDiG Duplicate File Deleter on your Windows or Mac. Choose the "Duplicates" feature and click "Get Started."
-
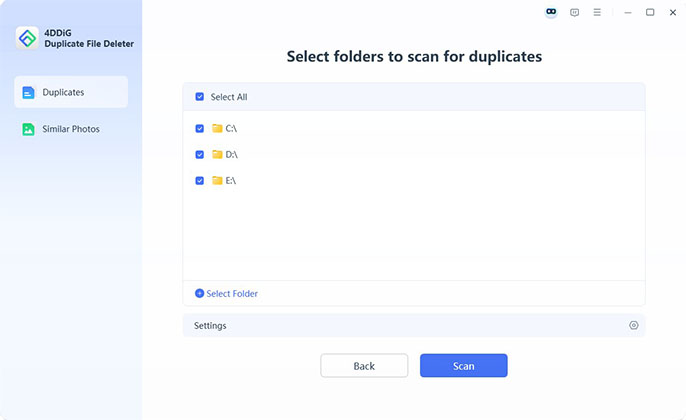
Select Drive or Folder to Scan
Choose Local Drive and click Next. Then continue to select the EpicGamesLauncher folder or any other target folder.
select epicgameslauncher drive and folder to scan duplicates
-
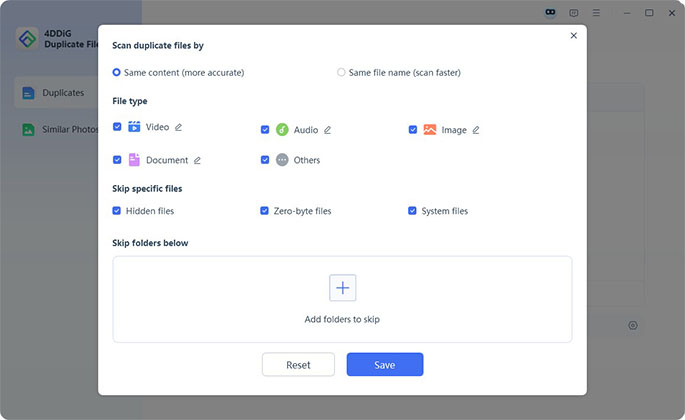
Customize Scan Settings
Click the Cog Settings icon to refine your scan. Adjust file types, exclude folders, or set the similarity threshold for near-duplicate images. Hit Scan once you're ready.
-
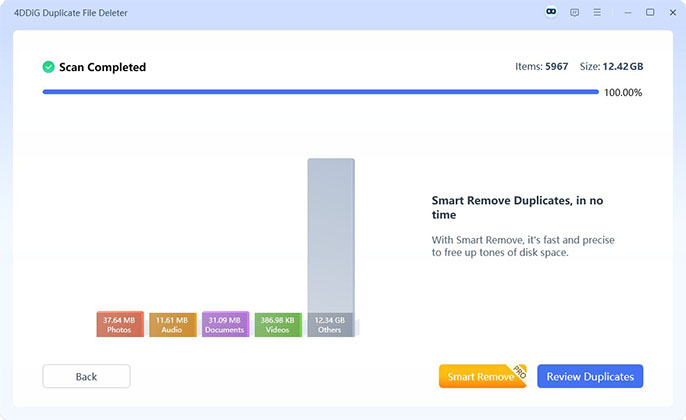
Remove Duplicate Files
After the scan, you can check how many duplicates were found by type. Use Smart Remove to automatically delete duplicates or click Review Duplicates to select manually. You can also use Auto Select to keep only the newest or largest files.
By following these steps, you can easily resolve the issue of can't install apps as /var/cache/apt/archives/ is full to avoid storage-related errors. Plus, 4DDiG offers a free option to remove up to 15 duplicates, making it a great option if you are looking to clean up space without commitment.
Part 3. How to Fix Not Enough Free Space in /var/cache/apt/archives [Common Ways]
Way 1. Check Size of /var/lib/vz/dump/ Folder and Move It to Another Storage
One of the most common reasons for running out of disk space in Proxmox, especially when trying to install or update packages, is the buildup of backup files in the /var/lib/vz/dump/ folder. This folder is where Proxmox stores backup images of containers and virtual machines. Over time, these files can grow in size and take up space on your root partition (/).
Proxmox stores backup files of your virtual machines and containers in the /var/lib/vz/dump/ folder. Over time, this folder can get very large and fill up your root disk (/), causing errors during updates or installations.
What to Do:
-
Check how much space this folder is using by typing: du -h /var/lib/vz/dump (This shows you the size of each file in the folder.)
-
If there are old or unused backup files, delete them to free up space.
-
If you still want to keep those backups, move them to another storage location like your NAS. For example, move them to /mnt/pve/QNAP_NAS if it's already mounted.
Once moved, delete them from the dump folder to clear space.
This is usually the fastest way to free up a large amount of disk space.
Way 2. Clear Space from Root Filesystem - Empty the apt Cache
If your system is throwing errors like, you don't have enough free space in /var/cache/apt/archives/, a quick and effective fix is to clear the APT cache. This cache stores package files from previous installations or updates, and it can grow quite large over time, especially if you're not regularly cleaning it.
What to Do:
-
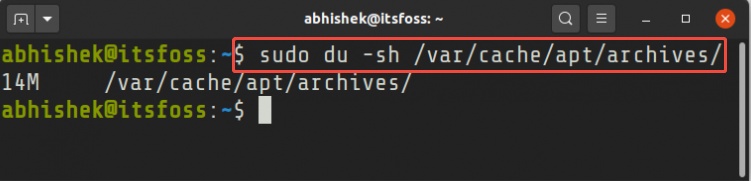
Delete the APT cache by typing: $ sudo du -sh /var/cache/apt/archives/. This safely removes old update files and can instantly free up space.

-
Check system log files — sometimes errors fill these logs up without you knowing. Go to the log folder: cd /var/log. Then list the files by size: ls -lahS. Look at the top of the list. If any files are very large (like in gigabytes), you can delete them or rotate them to prevent further issues.
-
Optional: If your system uses journalctl for logs, you can clean that up too: journalctl --vacuum-size=64M. This trims down your logs to a safe size.
This will show you which logs are the largest. If you find any massive ones, it's worth investigating why they’re growing so fast and either clearing or rotating them.
Part 4. FAQs
Q1: Can I delete files in var cache?
Yes, it’s generally safe to delete files in /var/cache, especially cached package files. These are temporary and will be recreated when needed.
Q2: Is it safe to remove the var cache apt archive?
Yes, deleting files from the /var/cache/apt/archives directory is safe. These are just downloaded packages that can be re-downloaded if needed.
Q3: Why does Docker build fail with the "you don't have enough free space in /var/cache/apt/archives/" error?
This happens when your root file system is full. It may also show errors if the archives directory /var/cache/apt/archives/partial is missing, which can break package installation steps.
Conclusion
If you're seeing the error, you don't have enough free space in /var/cache/apt/archives/, it's a sign your system's storage is full. It can happen due to cached files, logs, or duplicate data. You can do the regular cleanup, but they are a bit technical.
And for a faster and smarter solution, you should try 4DDiG Duplicate File Deleter. It quickly scans and removes unnecessary duplicate files, freeing up valuable space and keeping your system running smoothly.
Secure Download
Secure Download
💡 Summarize with AI:
You May Also Like
- Home >>
- Remove Duplicates >>
- You Don't Have Enough Free Space in var/cache/apt/archives/: What It Means & 3 Fixes
 ChatGPT
ChatGPT
 Perplexity
Perplexity
 Google AI Mode
Google AI Mode
 Grok
Grok